Smart Facility
Alarm Management
Alarm management is a set of rules which ensure that the events directly or indirectly impacting the electrical, mechanical or electromechanical infrastructures of the Smart Facility are leveled and are notified and reported to the manager or the facility shift staff through various communication methods (audio, email, sms etc.).
The Alarm Management System provides configuration management, short-term deviation (incident) detection, risk management in field activities, status assessment independent of people and higher operational performance.
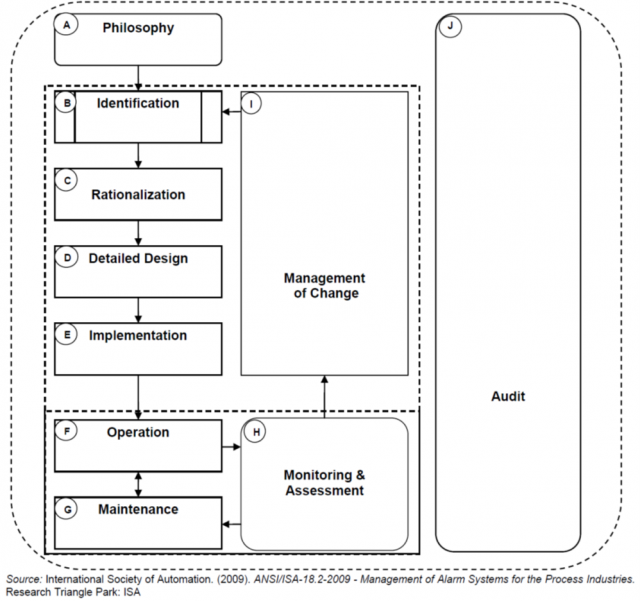
Figure: ISA-18.2 Alarm Life Cycle
Otomatica creates this in compliance with the ISA-18.2 standard, ensuring the most effective behavioral performance from the operation staff.
ISA-18.2 was prepared with a lifecycle consisting of ten stages (ref. Figure 1). These are:
Alarm Philosophy: Sets out the purposes of the alarm system and the business processes required to meet these objectives.
Identification: The required alarms are identified.
Rationalization: It is ensured that an alarm meets the demands specified in the alarm philosophy, including prioritization, classification, setting adjustment and documentation tasks.
Detailed Design: The process of designing the aspects of the alarm in a way that meets the requirements specified in the rationalization and the philosophy, requires certain decisions regarding human-machine interface (HMI) definitions, and specific or advanced techniques are used.
Implementation: The alarm design is rendered operational. This may involve commissioning, testing and training activities.
Operation: The alarm is operating. This stage includes refreshing training if necessary.
Maintenance: The alarm is not functioning due to test or repair activities. The behavior of the system during this period is decided.
Monitoring and Evaluation: The performance of the alarm system is monitored continuously and reported against the targets set in the alarm philosophy.
Change Management: Any changes in the alarm system are managed with a defined process.
Inspection: Periodic examinations are conducted in order to preserve the integrity of the alarm system and to protect the alarm management business processes.


